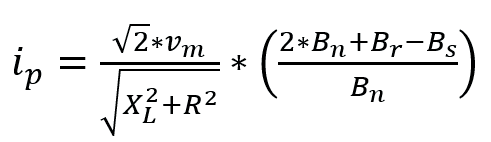Typical measurements of transformers include Transformer efficiency measurement , iron, copper and Magnetization loss Measurement and No-load characteristic Analysis and measurement of. And according to the different development stages or stages, the transformer needs to be measured many times.
>On line analysis of transformer efficiency
>Transient event analysis (e.g. inrush test up to 10 MS/s/ch)
>Protection class CAT IV 600 V/CAT III 1000 V
>High precision test under low power factor
>Can be integrated into existing Test bench
>Synchronously measure all inputs, such as voltage, current, temperature, vibration, etc

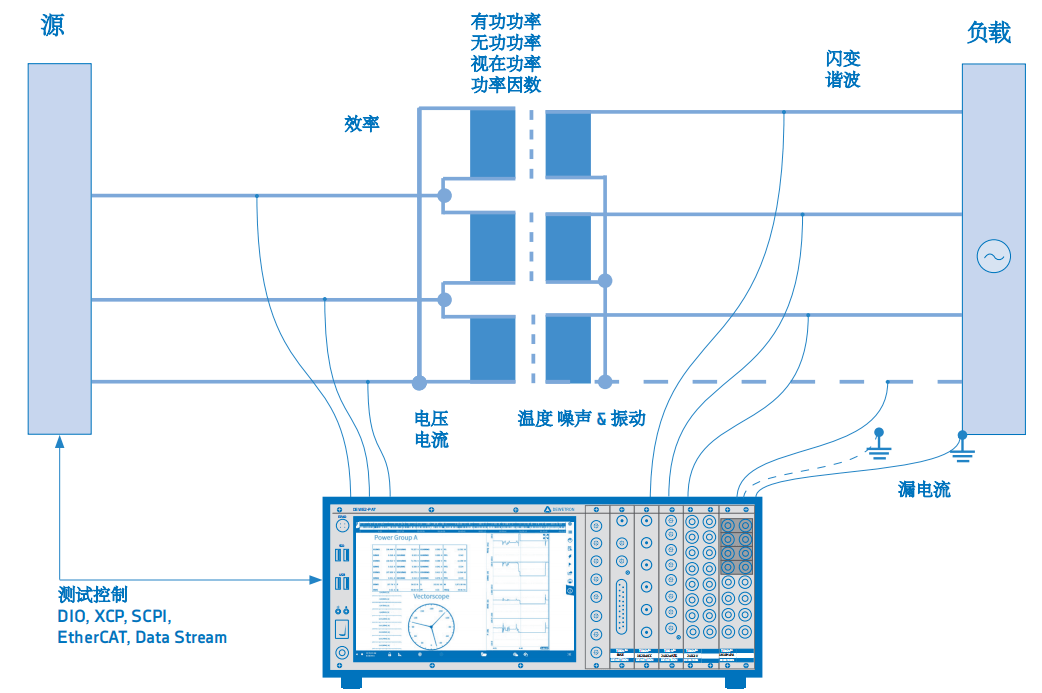
In order to accurately measure the efficiency of transformers, a high-end measurement system that can ensure high-precision measurement under low power factor (PF) is needed. The key here is to use the appropriate current sensor Perform low phase shift current measurement In addition, some standards may require that the measured power loss be temperature corrected. This requires additional simultaneous temperature measurements (windings, environment, airflow in and out, etc.) and corrections for the corresponding calculations. During or after the measurement, different factors can be correctly calculated through the mathematical functions in the data acquisition system software. You can also use the. mat export function of the software to calculate the correction value directly through MATLAB. For comprehensive analysis, the same measurement system can also be used to measure vibration and noise. In a word, combination DEWETRON power analyzer Or other data acquisition systems and DEWETRON Measurement software OXYGEN Combined, it is an ideal solution to accurately test transformer loss according to different standards.
In addition to high-precision measurement systems, it is recommended to use fully insulated input channels. For the safety of users and measuring systems, insulation requirements are not only applicable to voltage and current channels, but also to measuring channels for measuring temperature, vibration or other signals.

A typical measurement task may be one of the following:
>Efficiency analysis of different power values and loads
>Voltage ratio measurement and phase shift analysis
>Measurement of no-load loss and current
>On load tap changer test and magnetizing inrush current test
>Measure the power of fan and oil pump motor
>Measurement of no-load current harmonics
>Influence of frequency on efficiency
>Determination of transient voltage transmission characteristics
Challenges and requirements:
There are many difficulties and requirements related to these different types of measurements and requirements. The following lists some aspects that need to be focused on: > The whole measurement process needs high-precision test > The power factor remains high precision test within the range of 0.1 to 0.01 > Iron, copper and magnetization loss > Determination of no-load characteristics > On line efficiency measurement and calculation of different parameters > Additional simultaneous temperature, vibration and noise measurements
Application case WETRON
> Transformer efficiency under symmetrical load
> Iron loss assessment under no-load condition
> Copper loss assessment of short-circuit test
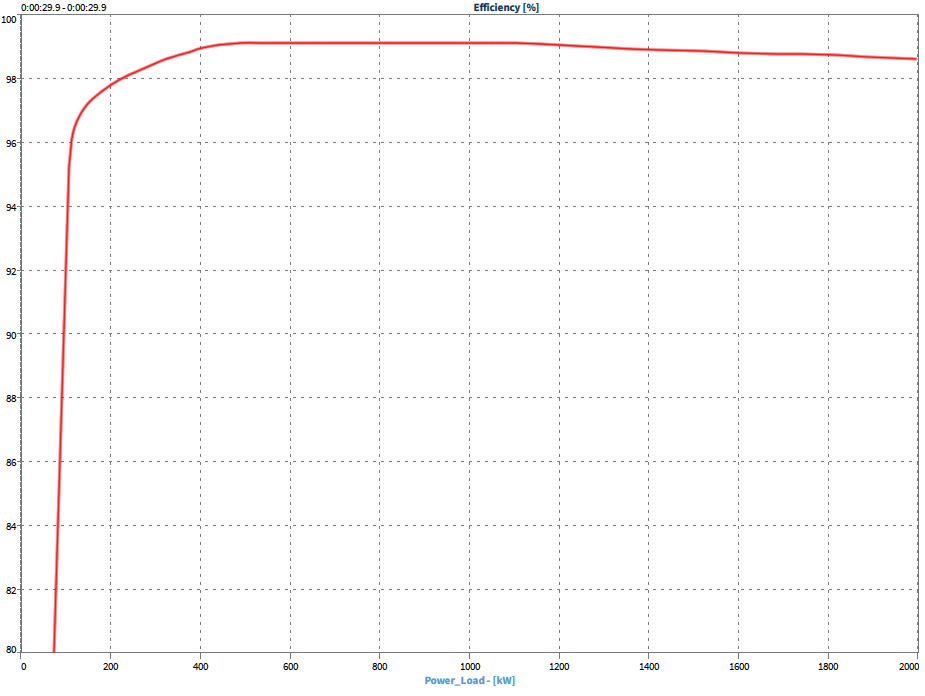
Efficiency analysis
In this example, DEWETRON Data acquisition and analysis software based on OXYGEN Used to analyze the efficiency of transformers. OXYGEN stay DEWETRON It can run on the power analyzer, and can conduct online calculation and analysis. These analyses (such as using efficiency charts) can be completed without stopping measurement.
Fast event analysis: inrush test
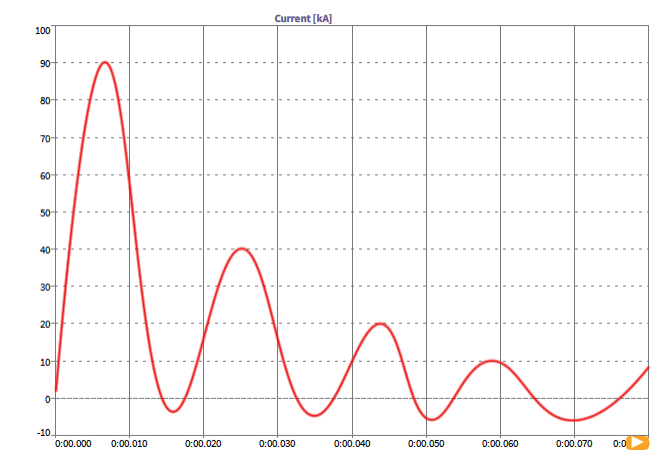
The magnetizing inrush current in transformer is caused by the sudden change of excitation voltage. The current in the transformer may be caused by regulating no-load transformer, external fault of transformer, voltage recovery process after clearing external fault, or out of phase synchronization of connected generator. Since the magnitude of inrush current may be as high as the short-circuit current, it is necessary to analyze the inrush current under various conditions in detail to understand the transformer protection system.
Surge peak current( ip )It depends on several parameters. It is proportional to the applied voltage, rated flux density, residual flux and saturated flux density of the transformer, and inversely proportional to the physical parameters of the transformer (such as total DC winding resistance and air core inductance of the transformer).
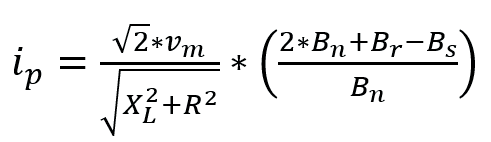
V m .... Apply voltage
X L ..... Inductive reactance
R ..... DC winding resistance of transformer
Bn ... Rated transformer flux density
Br .... Residual flux density of transformer
Bs .... Saturation flux density