When discussing measurement technology and signal processing, sampling rate , bandwidth Data throughput It is very important. In the last article, we introduced the sampling rate. Today, we will focus on bandwidth.
What is bandwidth?
Another key parameter in signal processing is bandwidth. It defines the width of the interval in the spectrum in terms of the upper and lower limits of frequency. It is usually measured in hertz. Bandwidth is a basic concept in communication engineering, radio engineering, acoustics and other fields. Therefore, the correct definition of the term may also vary depending on the field of application.
Broadly speaking, we distinguish between passband bandwidth and baseband bandwidth. The passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper cut-off frequency and the lower cut-off frequency, while the baseband bandwidth is only the upper cut-off frequency. However, for completeness, other differences related to bandwidth should be mentioned, such as relative bandwidth, x-dB bandwidth, and so on. In the context of Nyquist sampling rate, the term bandwidth usually refers to baseband bandwidth.
Bandwidth must be selected in the right way, just as the sampling rate limits the spectrum. We will use a short example to explain this:
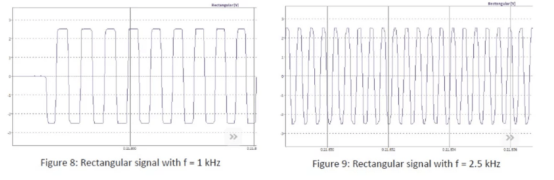
The rectangular signal scan is generated from 1 kHz to 30 kHz, and the sampling rate is 20 kHz. When the sampling rate remains unchanged (20 khz), the frequency of the reconstructed signal can reach 2 khz. The left figure shows the signal, while the rectangular signal can be clearly reconstructed when the initial frequency is 1 khz. At the frequency of 2.5 kHz, as shown in the figure, the rectangular signal is smoothed and looks more like a sine wave. This process continues until the signal can no longer be reconstructed.
summary
When choosing the perfect measurement settings for your application, you have to deal with a large number of characteristic parameters. The three key parameters are:
Sample Rate - Average number of samples of waveforms obtained per second
Bandwidth - interval width in the spectrum
Data rate - amount of data transferred per time





