When discussing measurement technology and signal processing, it is important to understand the various specifications and parameters to find the correct settings for your application. Therefore, in the next article, we will carefully study the following:
sampling rate
bandwidth
Data throughput
What is the sampling rate?
A crucial parameter is the sampling rate - also known as the sampling rate or sampling frequency. It is the average number of samples obtained per second for a waveform. The unit is the number of samples per second, sometimes Hz.
The sampling rate is used in the field of signal processing, where sampling is the process of reducing continuous time signals to discrete time signals. The resulting sample is a specific value of the signal at a specific point in time and/or space. In order to find an appropriate sampling rate, the Nyquist theorem between continuous signals and discrete signals must be satisfied.
Nyquist theorem - select the correct sampling rate
Theorem: "If a function f (t) does not contain a frequency higher than B Hz, it can be completely determined from its coordinates, and the interval between these points is less than 1/(2B) second. [Shannon, Claude E. (January 1949)]
Nyquist theorem is a part of the basis of signal conditioning. On the one hand, it can use continuous time signal to construct discrete time signal, on the other hand, it can reconstruct the original signal.
However, to achieve this, a sampling rate that is at least as high as the Nyquist rate must be selected. The Nyquist rate is equal to twice the frequency of the original signal. Although generally 10 times higher sampling rate is selected to ensure sufficient signal quality.
Here is a simple example:
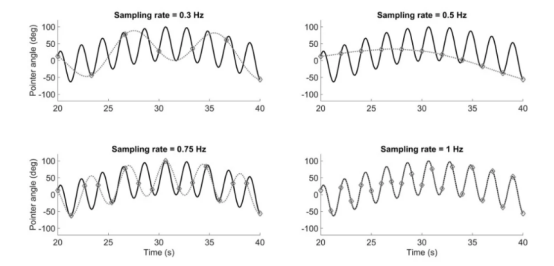
The following figure shows several sinusoidal signals. The black solid line describes the original signal with a frequency of~0.48 Hz. The highlighted marker indicates the sample point according to the selected sample rate. The gray dotted line represents the signal reconstructed according to the sampling rate. The Nyquist rate in this example is 0.96 Hz (2 * 0.48 Hz). The results show that the original signal can not be reconstructed for all cases with a sampling rate of 0.96 Hz; It can be recovered only when the sampling rate is 1 hz.
Undersampling and oversampling
Undersampling (or band-pass sampling) refers to the process of sampling the band-pass filter signal at a sampling rate lower than Nyquist's rate, but it can still be reconstructed.
Oversampling is a technique to sample signals at a sampling rate higher than Nyquist's rate. This can improve resolution and better SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio). In order to improve an additional resolution, the signal must be oversampled four times.
Note: The terms oversampling and undersampling are also used in the field of statistical data analysis, but they have different meanings. Note: There is a risk of confusion.
DEWETRON Measurement solutions for
DEWETRON is a manufacturer of high quality and modular measuring equipment. Our measurement systems are widely used in measurement applications, including aerospace, automotive, energy and manufacturing. We offer a variety of products to meet your needs. Start with all-in-one system, from mainframe to front-end and single measurement card. Look at our products and find the right equipment for you:
Integrated system
mainframe
Front end data acquisition
Measuring board
Since the quality of any measuring equipment depends on the software running on it, we also provide you with OXYGEN - our intuitive test and measurement software. It provides a variety of software packages, analysis tools, and monitoring options, and assists in the overall measurement process.





