Application of Dewicron data in phase field fracture modeling of monolithic and laminated glass under quasi-static bending
Application Introduction
This is an interesting application. Customers need to predict and model the initiation and propagation of glass cracks, especially for monolithic and laminated glass. It is completed by a mechanism specializing in mechanics. Laminated glass retains the optical quality and structural application of glass, while providing a certain level of post fracture resistance. This is particularly important. For example, after an earthquake, impact or similar disaster, the reliability of the structure is very important in the case of such unforeseen events, which can be increased through lamination. This research has always been a challenge in solid mechanics, but the phase field fracture and damage formulas used for modeling have become a powerful and mature tool for simulating brittle solid fracture. These methods can predict the initial stage of cracks and deal with complex crack patterns, providing good results for many problems. Research and understanding of its structural performance is the key factor to determine the crack initiation point and predict its growth. The resulting fracture mode can point out the cause of failure and provide important information for diagnosis and interpretation. Some examples of modes can be seen in the figure whether the mode corresponds to the overstress caused by uniform load, thermal stress, instability, nickel inclusion or soft and hard impact.
The group focused on bending of laminated glass before and after fracture. The aim is to predict the bending response of multilayer samples in terms of stress and deflection. The corresponding fracture mode is discussed and predicted by numerical model. The advantages and disadvantages of the phase field formula should be elaborated on the practical application of the fracture modeling of laminated glass. First, a numerical case study was conducted under bending, and different effects were observed. For example, the effect of dimension reduction. Then, experimental tests were carried out, including the material composition of laminated glass, material model test and quasi-static bending test.
Quasi static bending test
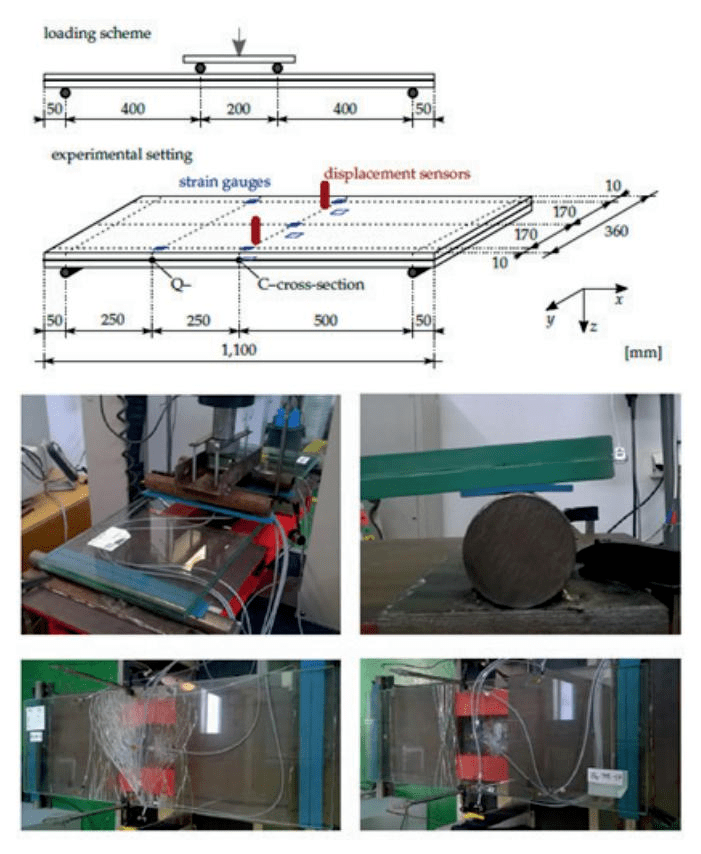
For the details of this study, a brief explanation of the quasi-static bending test will be given. Five annealed glass samples with ethylene vinyl acetate interlayer and five annealed glass samples with polyethylene butyraldehyde interlayer were tested. The samples are placed on a cylindrical support and separated by a rubber pad, as shown in Figure 7. The deflection was measured with two linear differential transformers. Eight strain gauges are attached to the surface, five are attached to the upper surface under compression, and three are attached to the lower surface under tension, as shown in the figure. In this test, the Dewetron data acquisition and measurement system is used for data acquisition, and the sampling rate is 10 Hz. In order to obtain the distribution of normal stress, strain gauges are placed longitudinally. In order to analyze the response before the first fracture and obtain the failure stress, three strain gauges were placed at the place with the maximum bending moment under tension. In order to monitor the behavior of glass after fracture, the other two groups of pressure gauges are placed on the upper surface for compression. The axial strain along the glass length can be measured by the arrangement of the quarter bridge strain gauge.
Experimental conclusion
After the experiment, the data are compared with the verification results of the phase field model. Because of the damage before crack identification, its nonlinear response is very important for some phase field formulas of glass under bending conditions. This may lead to overestimation of the response.
The comparison results show that the phase field model is in good agreement with the measured stress and resistance of laminated glass. However, using quasi-static analysis, only one or two cracks were located, but many cracks appeared during the experiment. The model must be extended by dynamic effects to realize the propagation of multiple cracks. In addition, the strength of glass should be considered to be randomly distributed between layers, and the team is currently expanding the model.
Product recommendation
Dewei Chuang Front end data acquisition equipment TRIONet

TRIONet is a compact front-end solution for synchronous high-speed data acquisition across long distances and distributed locations. The front-end system communicates with the OXYGEN Visual operation.
TRIONet can connect to any Windows computer via USB or Ethernet. In addition, TRIONet system is the high-speed channel expansion of other DEWETRON DAQ data acquisition systems, which can use Ethernet interconnection.
You only need one TRIONet to realize multiple mixed signal inputs, such as:
Isolated high voltage and current inputs
High performance auxiliary input
CAN interface
Test bench integrated signal
Counter










